Today we are going to model mixed numbers, it’s a piece of cake. Recall that a mixed number is a number containing a whole number and a proper fraction. To model a mixed number, first, we are going to model the whole number and then the improper fraction (a fraction where the numerator is less than the denominator). In this post we will see some examples.
Content:
1) Model 21⁄3
In this example, we will use rectangles to represent our mixed number. One rectangle represents 1 whole. So first, we will draw 2 rectangles to represent 2 wholes and shade them completely. Finally, we will model the proper fraction 1⁄3, we just need to divide one more rectangle into 3 equal parts and then shade 1 of those parts.

If you don’t want to use rectangles, you can also use circles or other geometric figures.

2) Model 32⁄5
This time we will use circles to model our mixed number. First, we are going to model the whole number (3), and then the proper fraction. One circle represents 1 whole, to model 3 wholes we need to draw 3 circles and shade them completely. Finally, we model the proper fraction 2⁄5.
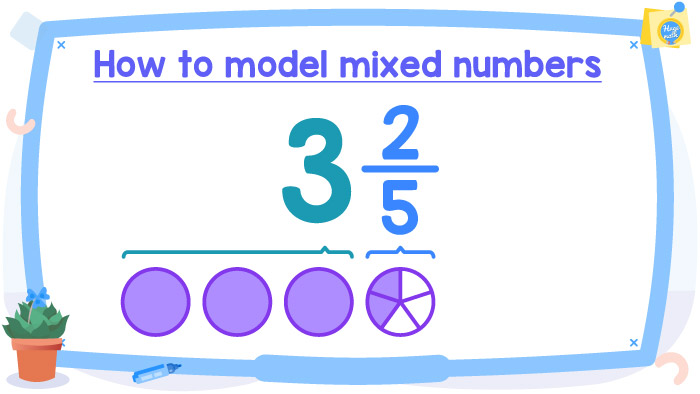
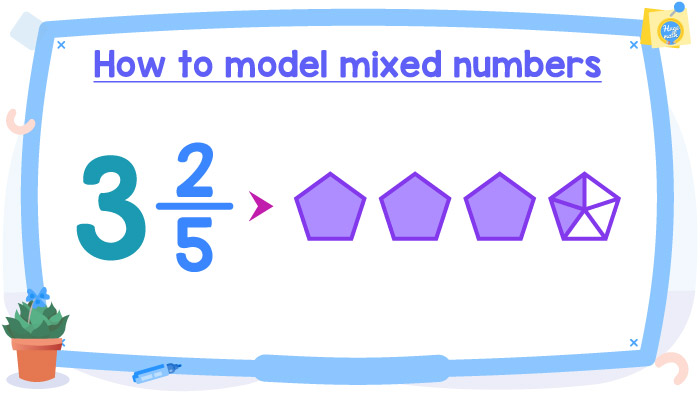
And that’s it! If you don’t want to use circles, you can also use pentagons, rectangles, or other geometric figures.
Homework
In the following image, each square represents 1 whole. Write a mixed number to represent the shaded portion.

Video
In the next video, we will see more examples.
References
For this lesson, we have used these books:
- Aufmann, R. y Lockwood, J. (2014). Basic College Mathematics (10th ed., pp. 70-71). Cengage Learning.
- Tussy, K., Gustafson, D. y Koenig, D. (2013). Prealgebra (4th ed.; pp. 360-361). Cengage Learning.
- Martin-Gay, E. (2020). Basic college mathematics with early integers (4th ed; p. 180). Pearson.